acl and pcl tear test|acl vs pcl usmle : online sales The Lachman test is a specific clinical exam technique used to evaluate patients with a suspected anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury. The test relies on proper positioning . Resultado da 3 de ago. de 2023 · O grupo Estado Islâmico (EI) confirmou nesta quinta-feira a morte do seu líder, Abu al-Hussein al-Husseini al-Qurashi, em um .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Os hambúrgueres da Nomad são clássicos, sem frescura. É como banda de rock com guitarra, baixo e bateria. É como futebol jogado com dois pontas e o time todo de .
Varus stress test for Lateral Collateral Ligament. In the varus stress test, the examiner adducts and internally rotates the lower leg to assess the stability of the lateral collateral ligament (LCL). Apley’s Distraction Test. . The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) are two major ligaments in the knee that work together to provide stability. They are also common sites of serious tears, particularly in athletes. PCL injuries are traumatic knee injuries that may lead to posterior knee instability and often present in combination with other ipsilateral ligamentous knee injuries (i.e PLC, ACL). Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with a .
iphone x spigen case drop test
The Lachman test is a specific clinical exam technique used to evaluate patients with a suspected anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury. The test relies on proper positioning . ACL tears are common athletic injuries leading to anterior and lateral rotatory instability of the knee. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with presence of a traumatic knee effusion with increased laxity on Lachman's test .
An MRI can show the extent of an ACL injury and signs of damage to other tissues in the knee, including the cartilage. Ultrasound. Using sound waves to visualize internal . Anterior Drawer Test (ACL): Similar to the Lachman test, the anterior drawer test assesses anterior tibial displacement with the knee flexed at 90 degrees. Increased anterior translation can indicate ACL injury. Posterior .Even though your PCL is stronger and larger than your anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), it can still be injured. People with a PCL injury may have pain, swelling and other symptoms. .
anterior cruciate ligament. ( ACL. ), posterior cruciate ligament. ( PCL. ), medial collateral ligament. ( MCL. ), and. lateral collateral ligament. ( LCL. ) result in knee pain and . The Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) is one of the four major ligaments of the knee joint that functions to stabilize the tibia on the femur. It originates from the anterolateral aspect of the medial femoral condyle in the area of the intercondylar notch and inserts onto the posterior aspect of the tibial plateau. It functions to prevent posterior translation of the tibia on .
Clinical trials. Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.. Preparing for your appointment. The pain and disability associated with an ACL injury prompt many people to seek immediate medical attention. Others may make an appointment with their family doctors.The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is located inside your knee joint. It can become injured when the ligament is torn or stretched. . Posterior cruciate ligament injuries are far less common than ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) tears. In fact, PCL injuries make up less than 20% of all knee ligament injuries. Most commonly, PCL tears occur . ACL tears are common athletic injuries leading to anterior and lateral rotatory instability of the knee. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with presence of a traumatic knee effusion with increased laxity on Lachman's test but requires MRI studies to confirm diagnosis. . posterior cruciate ligament and posterolateral corner injuries. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of 2 cruciate ligaments that aids in stabilizing the knee joint. It is a strong band made of connective tissue and collagenous fibers that originate from the anteromedial aspect of the intercondylar region of the tibial plateau and extends posterolaterally to attach to the medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle, where there are .
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), is one of four ligaments important to the stability of the knee joint. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), sits just in front of the PCL.The ACL is much better known, in part because ACL tears are much more commonly diagnosed than injuries to the PCL. Interestingly, it is thought that PCL injuries account for up to 20 percent .The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is the strongest and largest intra-articular ligament in human knee and the primary posterior stabilizer of the knee. It comprises of 2 functional bundles: the larger anterolateral bundle (ALB) and the smaller posteromedial bundle (PMB). The size of the femoral attachment of the ALB is nearly twice the size of its tibial attachment[1].
Understanding the anatomy and purpose of the ACL is crucial for athletes and individuals alike, as it can help in injury prevention and guide rehabilitation efforts in the event of an ACL tear. Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is the other cruciate ligament in the knee joint.
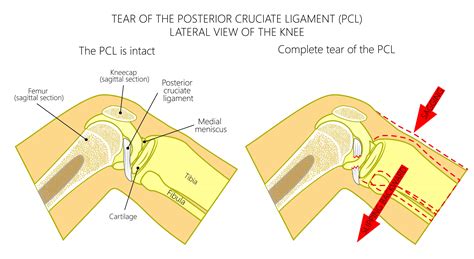
The ACL is located in the center of the knee and works with the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) to stabilize the front-to-back movement of the knee. . the test is negative. Can ACL tears be treated without surgery? . Ma Y, Black BR, Fung S, Lyman S. Cartilage injury after acute, isolated anterior cruciate ligament tear: immediate and . PCL injuries are traumatic knee injuries that may lead to posterior knee instability and often present in combination with other ipsilateral ligamentous knee injuries (i.e PLC, ACL). Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with a traumatic knee effusion and increased laxity on a posterior drawer test but requires an MRI for confirmation.The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is located inside the knee, just behind the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). It is one of several ligaments that connect the femur (thighbone) to the tibia (shinbone). The posterior cruciate ligament keeps the tibia from moving backward with relation to the thigh bone.
Overview [3]. Both ACL injury and PCL injury may present initially as acute internal knee derangement, reducing the yield of physical examination maneuvers. The diagnosis is typically confirmed via MRI, which can have variable findings depending on the mechanism and associated injuries.They occur less frequently than anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries as the PCL is broader and stronger. Clinically Relevant Anatomy . Dial test or tibial external rotation test: to test if there is a combined PCL and posterolateral corner (PLC) injury. . Posterior cruciate ligament injuries in trauma patients. Arthroscopy: The Journal . Lachman’s test is an alternative test assessing for laxity or rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). This test is rarely required in an OSCE scenario, with the anterior drawer test being the preferred method of ACL assessment. . PCL injury typically occurs secondary to hyperflexion of the knee joint (e.g. a fall onto a flexed knee).
Grade 1 and 2 ligament injuries (partial tears) don't require surgery to repair and are usually treated with some combination of rest, elevation, pain management, and physical therapy.; Grade 3 injuries indicate a complete .The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is behind the ACL. The cruciate ligaments control the way your knee moves front to back. Advertisement. . ACL, PCL, MCL and LCL. Injuries to the knee ligaments are common, especially in athletes. A sprained knee can range from mild to severe. Talk to a healthcare provider if you have a severe knee injury .Clinical Note [edit | edit source]. This examination must be performed with particular care because the start position could result in a false-positive anterior drawer test result for the anterior cruciate ligament, if a posterior sag (an indication of a posterior cruciate problem) goes unnoticed before the test is started. If minimal or no swelling is present, the sag is evident .
While both ACL and PCL tears can be painful initially, the real problem is the lingering instability of the knee joint. The severity of the tear is key. One can overcome the discomfort and instability of a partial tear with systematic and focused rehabilitation of the musculature surrounding the knee. But if the ligament is completely ruptured .
Another test used to diagnose ACL injuries is the Lachman test. The same 2013 study reports the Lachman test has a sensitivity of about 94 percent. The same 2013 study reports the Lachman test has . The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is a ligament within the knee.Ligaments are tough bands of tissue that connect bones. The PCL -- similar to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) -- connects .
Your ACL is a ligament located on the front (anterior) side of your knee. It crosses with another ligament (the posterior cruciate ligament, or PCL) to help stabilize your knee and prevent . There are an estimated 80,000 to 100,000 anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) repairs in the United States each year. Most ACL tears occur from noncontact injuries. Women experience ACL tears up to .Lachman test and anterior draw test for anterior cruciate ligament injuries. Posterior draw test for posterior cruciate ligament injuries. Specific tests for meniscal injuries (McMurray, Thessaly, Apley) are not recommended as they have particularly poor diagnostic accuracy, especially in non-specialist settings.The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is a ligament in each knee of humans and various other animals. It works as a counterpart to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). It connects the posterior intercondylar area of the tibia to the medial condyle of the femur.This configuration allows the PCL to resist forces pushing the tibia posteriorly relative to the femur.
A positive anterior drawer test indicates possible ACL injury, whereas a positive posterior drawer test indicates possible PCL injury. The pivot shift test involves internally rotating the tibia, applying valgus pressure to the knee, then flexing the knee. The ACL connects your thigh bone (femur) with your shinbone (tibia) and works in tandem with your posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) to allow you to move your knee back and forth. If you've had an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury, your healthcare provider may recommend rehabilitation exercises to help improve your knee health. An ACL injury is often caused by overstretching or tearing this ligament in the middle of the knee. It can affect the stability of your knee and .
what is a pcl rupture
Resultado da AUD-20231218-WA0002
acl and pcl tear test|acl vs pcl usmle